算法 4th 连通性问题
前言
最近又将之前买上的《算法》拾了起来,打算好好读读,后悔当初买上没有好好看,现在看来,真的是一本好书,让人着迷。
结合着 Coursear 上的课程,尝试完成了第一个编程作业。
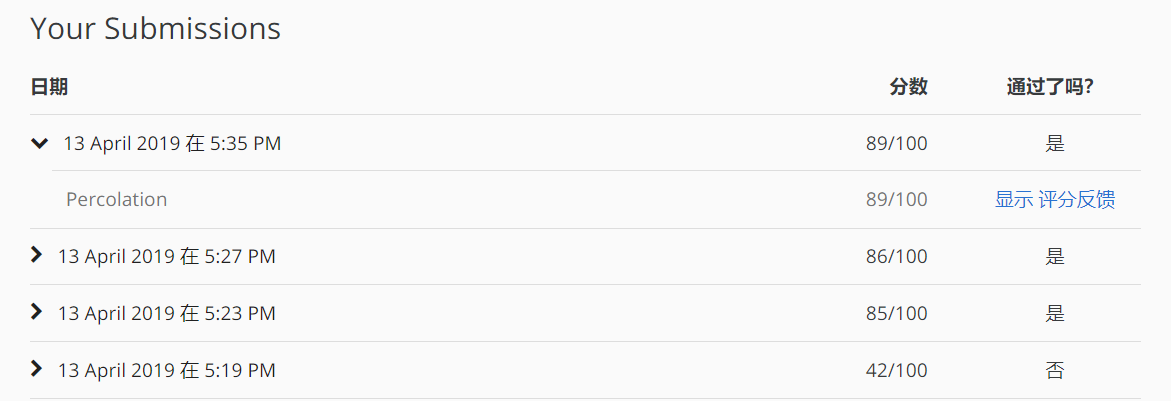
经过多次提交分数才达到 89 分
准备
经过一周的学习发现,要做这周的编程题,首先要把这一章书籍内容自习看一遍,把书上写的算法代码可以看懂,并且可以写出来。书上内容阅读完成再看视频,视频会介绍书上的内容并和后面的习题有一些思路提示。
为了能完成作业需要下载与书籍配套的 algs4.jar 包,以编写代码。
试题
这是一个连通性问题,和最后一个视频课中提及的问题一样,只不过需要用算法写出来。
该题包含两个问题
构建一个可以渗透的网格
你需要编写一个 Percolation 类来进行构建,要实现下面的 API
public class Percolation {
public Percolation(int n) // create n-by-n grid, with all sites blocked
public void open(int row, int col) // open site (row, col) if it is not open already
public boolean isOpen(int row, int col) // is site (row, col) open?
public boolean isFull(int row, int col) // is site (row, col) full?
public int numberOfOpenSites() // number of open sites
public boolean percolates() // does the system percolate?
public static void main(String[] args) // test client (optional)
}分别解释一下每个方法的意思。
Percolation(int n) 该方法是该类的构造器,要传入一个 n 用来构建一个 n × n 大小的网格。
open(int row,int col) 打开行为 row 列为 col 的格子,新构建的网格默认为全部关闭,我们需要通过这个方法打开表格。
isOpen(int row,int col) 检查这个坐标的网格是否处于 open 状态。
isFull(int row,int col) 检查从顶部到该网格是否连通。
numberOfOpenSites() 返回有多少网格处于 Open 状态。
percolates() 返回网格是否从上到下是否连通。
在视频里讲到可以把方格上下虚拟出来一个格子,只要证明上方虚拟格子连通就可以证明连通。

思路
当我们要检查网格之间是否连通时,可以用到书上关于连通性的算法,algs4.jar 里已经有加权连通性的算法实行,我们可以直接使用。
需要一个数组来进行初始化网格,这里用 sites 数组,将网格的初始值存放进去。使用一维数组来保存该网格数据,同时长度要比要求长两位,用来表示虚拟头部和虚拟底部,将这两个点默认为打开(open)
在将一个网格打开(open)的同时 openSites 进行计数,要将要将它与周围网格进行连通。首先考虑第一行和最后一行,有打开状态的就将它与虚拟头部或虚拟底部进行连通。之后在考虑其他的网格和它的周围(上,下,左,右)进行连通。
代码
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.WeightedQuickUnionUF;
public class Percolation {
private final WeightedQuickUnionUF uf;
private final int n;
private int[] sites;
private int openSites = 0;
// create n-by-n grid, with all sites blocked
public Percolation(int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.n = n;
uf = new WeightedQuickUnionUF(n * n + 2);
sites = new int[n * n + 2];
for (int i = 0; i < sites.length; i++) {
sites[i] = 0;
}
sites[0] = 1;
sites[sites.length - 1] = 1;
}
// open site (row, col) if it is not open already
public void open(int row, int col) {
if (row > n || col > n || row < 1 || col < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if (!isOpen(row, col)) {
int index = (row - 1) * n + col;
sites[index] = 1;
openSites++;
if (row == 1) {
uf.union(0, col);
}
if (row == n) {
uf.union(sites.length - 1, index);
}
if (row < n) {
// connected bottom
if (isOpen(row + 1, col)) {
int newIndex = row * n + col;
uf.union(index, newIndex);
}
}
if (row > 1) {
// connected top
if (isOpen(row - 1, col)) {
int newIndex = (row - 2) * n + col;
uf.union(index, newIndex);
}
}
if (col < n) {
if (isOpen(row, col + 1)) {
int newIndex = (row - 1) * n + col + 1;
uf.union(index, newIndex);
}
}
if (col > 1) {
// connected top
if (isOpen(row, col - 1)) {
int newIndex = (row - 1) * n + col - 1;
uf.union(index, newIndex);
}
}
}
}
// is site (row, col) open?
public boolean isOpen(int row, int col) {
if (row > n || col > n || row < 1 || col < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
int index = (row - 1) * n + col;
return sites[index] == 1;
}
// is site (row, col) full?
public boolean isFull(int row, int col) {
if (row > n || col > n || row < 1 || col < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if (isOpen(row, col)) {
int index = (row - 1) * n + col;
return uf.connected(0, index);
} else {
return false;
}
}
// number of open sites
public int numberOfOpenSites() {
return openSites;
}
// does the system percolate?
public boolean percolates() {
return uf.connected(0, sites.length - 1);
}
}蒙特卡洛模拟
当我们构建的 sites 中的网格不断为 open 状态的时候,当多少个网格状态成为 open 的时候该网格成为连通状态。计算蒙特卡洛模拟连通的阈值。

蒙特卡洛模拟也是先实现下面的 API
public class PercolationStats {
public PercolationStats(int n, int trials) // perform trials independent experiments on an n-by-n grid
public double mean() // sample mean of percolation threshold
public double stddev() // sample standard deviation of percolation threshold
public double confidenceLo() // low endpoint of 95% confidence interval
public double confidenceHi() // high endpoint of 95% confidence interval
public static void main(String[] args) // test client (described below)
}PercolationStats(int n, in trails) 这个是个构造函数,在初始化对象的时候传入构造网格的 n 和训练次数。
mean() 用于计算平均值
stddev() 用于计算标准差
confidenceLo() 计算置信区间下限
confidenceHi() 计算置信区间上限
思路
关于计算平均值,标准差,置信区间的公式试题上已经说明,而且在计算平均值和标准差的时候可以使用 algs4.jar 包中的 StdStats API。
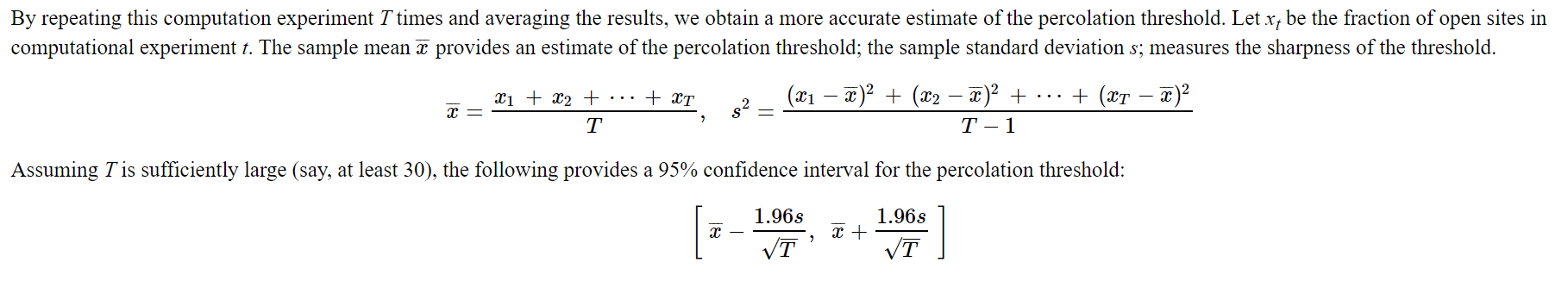
我们要计算当打开多少个 site 的时候, 该网格处于连通状态。我们要做的就是不断的打开每个 site ,并且记录对应的值。 xi 数据记录渗透率。整体上不算难,只要我们使用前一问的 Percolation 类就可以很快的写出该构造函数。
代码
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdStats;
public class PercolationStats {
private Percolation percolation;
private int trials;
private final double[] xi;
// perform trials independent experiments on an n-by-n grid
public PercolationStats(int n, int trials) {
if (n <= 0 || trials <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.trials = trials;
xi = new double[trials];
for (int i = 0; i < trials; i++) {
percolation = new Percolation(n);
int count = 0;
while (true) {
int col = StdRandom.uniform(1, n + 1);
int row = StdRandom.uniform(1, n + 1);
if (!percolation.isOpen(row, col)) {
percolation.open(row, col);
count++;
boolean isP = percolation.percolates();
if (isP) {
double x = count * 1.0 / (n * n);
xi[i] = x;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// sample mean of percolation threshold
public double mean() {
return StdStats.mean(xi);
}
// sample standard deviation of percolation threshold
public double stddev() {
return StdStats.stddev(xi);
}
// low endpoint of 95% confidence interval
public double confidenceLo() {
return mean() - (1.96 * stddev()) / Math.sqrt(trials);
}
// high endpoint of 95% confidence interval
public double confidenceHi() {
return mean() + (1.96 * stddev()) / Math.sqrt(trials);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = StdIn.readInt();
int t = StdIn.readInt();
PercolationStats ps = new PercolationStats(n, t);
StdOut.println("mean =" + ps.mean());
StdOut.println("stddev = " + ps.stddev());
StdOut.println("95% confidence interval = [" + ps.confidenceLo() + ", " + ps.confidenceHi() + "]");
}
}总结
这个题的两个问题层层递进,将计算渗透率的问题化解问两个问题,并且在第一问中还会使用到前面的连通性计算的问题,并且在问题的分解上和书籍一样,先给出每个方法的 API,我们只要去实现对应API即可,可见设计该问题时候作者的用心。
相关内容
如果你觉得这篇文章对你有所帮助,欢迎赞赏~
赞赏