String源码剖析
String 是 java 程序中出现比较多的对象,分析一下 String 首先 String 是由 final 修饰的。因此 String 不可变,无法继承。
将方法或类声明为final主要目的是:确保它们不会再子类中改变语义。String类是final类,这意味着不允许任何人定义String的子类。换言之,如果有一个String的引用,它引用的一定是一个String对象,而不可能是其他类的对象。——《Java核心技术 卷I》作者:R eversal
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/31345592/answer/51639967 来源:知乎 著作权归作者所有,转载请联系作者获得授权。
String不可变性及其原因
String的不可变性
什么叫String的不可变性呢?让我们来看一个例子。
String s=“abcd“;
上面的语句定义了一个字符串变量s,该变量指向字符串“abcd”,当初始化变量s时,会在堆中为s非配内容空间,当将字符串变量,赋值给另一个字符串变量时,例如:String s2=s;
此时,s2和s是相同的字符串对象,它们指向堆中的同一个内存空间。
当一个字符串连接其他字符时,他就指向了新的字符串对象,例如,s=s.concat(“ef“), 此时,s=“abcdef”;它在内存中又指向了一个新的储存空间,存放字符串"abcdef”。
当一个字符串在堆中被分配内容时,它就是不可变的,任何String的方法都无法改变字符串本身,但它可以返回一个新的字符串对象。
由于String是不可变的,所以他们的空间可以共享。例如String str = “abc”;就和
JAVA
char data[] = {‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’};
String str = new String(data);
是等价的,它们共享一个存储空间。如果需要可以修改的字符串对象,可以使用StringBuffer和StringBuilder,StringBuffer是线程安全的,由于StringBuilder不需要进行同步操作,StringBuilder是比较快速的。
- String不可变性的原因
- 源码中String的本质是一个final类型的char数组,既然是final类型,那个该数组引用value就不允许再指向其他对象了,因此只从类的设计角度讲:如果jdk源码中并没有提供对value本身的修改,那么理论上来讲String是不可变的
- 字符串池(String pool)的需求 在Java中,当初始化一个字符串变量时,如果字符串已经存在,就不会创建一个新的字符串变量,而是返回存在字符串的引用。 例如: String string1=“abcd”; String string2=“abcd”; 这两行代码在堆中只会创建一个字符串对象。如果字符串是可变的,改变另一个字符串变量,就会使另一个字符串变量指向错误的值。
- 缓存字符串hashcode码的需要 字符串的hashcode是经常被使用的,字符串的不变性确保了hashcode的值一直是一样的,在需要hashcode时,就不需要每次都计算,这样会很高效。
- 出于安全性考虑 字符串经常作为网络连接、数据库连接等参数,不可变就可以保证连接的安全性。
签名(signature)
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequenceString使用了
- 标记接口 java.io.Serializable
- 标记接口 Comparable
- 标记接口 CharSequenc
Compareable接口
public interface Comparable<T> {
public int compareTo(T o);
}此接口强行对实现它的每个类的对象进行整体排序。此排序被称为该类的自然排序,类的 compareTo 方法被称为它的自然比较方法 。
CharSequence接口
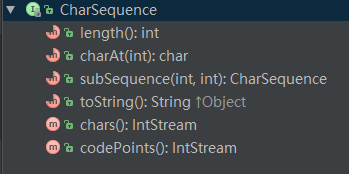 CharSequence的所有成员变量和方法。
CharSequence的所有成员变量和方法。
成员变量
- private final char value[];//这是用于存储String字符的数组
- private final int offset;//这是value数组的第一个有效的字符的index
- private final int count;//这是String中的字符个数
- private int hash; // 存储String的hashcode,默认是0
- private static final long serialVersionUID = -6849794470754667710L;//在进行反序列化时,JVM会把传来的字节流中的serialVersionUID与本地相应实体(类)的serialVersionUID进行比较,如果相同就认为是一致的,可以进行反序列化,否则就会出现序列化版本不一致的异常
源码剖析
构造器
String类的构造器有十六个,除了提供了一个无参构造函数之外,还有十五个带参构造器。
String()
public String() {
this.value = "".value;
}初始化一个新创建的 String 对象,使其表示一个空字符序列。注意,由于 String 是不可变的,所以无需使用此构造方法
String(String)
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.hash = original.hash;
}初始化一个新创建的 String对象,使其表示一个与参数相同的字符序列;换句话说,新创建的字符串是该参数字符串的副本。由于 String 是不可变的,所以无需使用此构造方法,除非需要 original 的显式副本。
String(char)
public String(char value[]) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
}分配一个新的 String,使其表示字符数组参数中当前包含的字符序列。该字符数组的内容已被复制;后续对字符数组的修改不会影响新创建的字符串。
String(char,int,int)
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= value.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
if (offset > value.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}作用为分配一个新的value,将传入的char数组进行一次复制,offset是开始索引位置,count表示数组长度。
String(int,int,int)
public String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= codePoints.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > codePoints.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
final int end = offset + count;
// Pass 1: Compute precise size of char[]
int n = count;
for (int i = offset; i < end; i++) {
int c = codePoints[i];
if (Character.isBmpCodePoint(c))
continue;
else if (Character.isValidCodePoint(c))
n++;
else throw new IllegalArgumentException(Integer.toString(c));
}
// Pass 2: Allocate and fill in char[]
final char[] v = new char[n];
for (int i = offset, j = 0; i < end; i++, j++) {
int c = codePoints[i];
if (Character.isBmpCodePoint(c))
v[j] = (char)c;
else
Character.toSurrogates(c, v, j++);
}
this.value = v;
}方法
checkBounds()方法
private static void checkBounds(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length) {
if (length < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(length);
if (offset < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
if (offset > bytes.length - length)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + length);
}这是一个私有的静态方法用于检查边界的方法。
length()方法
获得长度的方法
public int length() {
return value.length;
}isEmpty()方法
检查字符串长度是否是0,当长度为0返回true,否则返回false。
public boolean isEmpty() {
return value.length == 0;
}charAt()方法
该方法返回的值为char数组中的其中一个。
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return value[index];
}codePointAt()方法
用于返回指定索引处的字符,与codePointBefore方法类似,codePointBefore返回的的是索引之前的值
codePointAt
public int codePointAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return Character.codePointAtImpl(value, index, value.length);
}codePointBefore
public int codePointBefore(int index) {
int i = index - 1;
if ((i < 0) || (i >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return Character.codePointBeforeImpl(value, index, 0);
}equals()方法
首先equals返回的为一个boolean值。
instanceof是一个java的二元操作符,作用是检查左面是否为右面的实例化。返回值是boolean类型。
该方法是将一个传入对象进行一次复制,将复制对象的字符数组与原对象的字符数组进行比较。
这样就确保equals比较的是内容。这样就和==有了区分
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}compareTo()方法
按字典顺序比较两个字符串,如果相通返回0,如果不同返回他们之间的差值。 同样是通过字符数组进行比较。
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
return len1 - len2;
}### compare()方法
private static class CaseInsensitiveComparator
implements Comparator<String>, java.io.Serializable {
// use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.2.2 for interoperability
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8575799808933029326L;
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
int n1 = s1.length();
int n2 = s2.length();
int min = Math.min(n1, n2);
for (int i = 0; i < min; i++) {
char c1 = s1.charAt(i);
char c2 = s2.charAt(i);
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toUpperCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toUpperCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
c1 = Character.toLowerCase(c1);
c2 = Character.toLowerCase(c2);
if (c1 != c2) {
// No overflow because of numeric promotion
return c1 - c2;
}
}
}
}
return n1 - n2;
}
/** Replaces the de-serialized object. */
private Object readResolve() { return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER; }
}startsWith()方法
检查前缀是否匹配。
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) {
char ta[] = value;
int to = toffset;
char pa[] = prefix.value;
int po = 0;
int pc = prefix.value.length;
// Note: toffset might be near -1>>>1.
if ((toffset < 0) || (toffset > value.length - pc)) {
return false;
}
while (--pc >= 0) {
if (ta[to++] != pa[po++]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}hashCode()方法
返回String的hashCode,hashCode的计算方法是s[0]*31^(n-1) + s[1]*31^(n-2) + ... + s[n-1]
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}indexOf方法
indexOf一共有六个构造方法。
返回字符出现在字符串中第一次的位置。
public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
final int max = value.length;
if (fromIndex < 0) {
fromIndex = 0;
} else if (fromIndex >= max) {
// Note: fromIndex might be near -1>>>1.
return -1;
}
if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {
// handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a
// negative value (invalid code point))
final char[] value = this.value;
for (int i = fromIndex; i < max; i++) {
if (value[i] == ch) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
} else {
return indexOfSupplementary(ch, fromIndex);
}
}substring()方法
截取代码中的片段,值得注意的是在最后的返回值中它会new一个新String类。
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
if (endIndex > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex);
}
int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == value.length)) ? this
: new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}concat()方法
该方法主要用于连接字符串,Api文档中的例子
“cares”.concat(“s”) returns “caress”
从功能上看concat和+是类似的。但是他们之间使用区别的。
concat只能连接字符串,如果要连接其他类型要转化为String。
+可以连接非字符串。
如果长度为0返回原来的数组,否则就new一个数组。
public String concat(String str) {
int otherLen = str.length();
if (otherLen == 0) {
return this;
}
int len = value.length;
char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen);
str.getChars(buf, len);
return new String(buf, true);
}### replace()方法
replace用于替换String中的字符。 先用if来判断,来减少不必要的循环。
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) {
if (oldChar != newChar) {
int len = value.length;
int i = -1;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
while (++i < len) {
if (val[i] == oldChar) {
break;
}
}
if (i < len) {
char buf[] = new char[len];
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
buf[j] = val[j];
}
while (i < len) {
char c = val[i];
buf[i] = (c == oldChar) ? newChar : c;
i++;
}
return new String(buf, true);
}
}
return this;
}### split
### replaceAll
join()方法
这个是jdk1.8的新方法,让我们分析一下。 join的作用:通过一个字符或字符串来连接其他字符 注释文档的例子:
String message = String.join("-", “Java”, “is”, “cool”); // message returned is: “Java-is-cool”
官方文档中的注释提示
** Note that if an element is null, then {@code “null”} is added.**
public static String join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence... elements) {
Objects.requireNonNull(delimiter);
Objects.requireNonNull(elements);
// Number of elements not likely worth Arrays.stream overhead.
StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(delimiter);
for (CharSequence cs: elements) {
joiner.add(cs);
}
return joiner.toString();
}### toLowerCase()方法
该方法是将传入的字符串转化为一个小写的字符串。
这里有一个scan,这个scan是一个标签,用于跳出循环。
public String toLowerCase(Locale locale) {
if (locale == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
int firstUpper;
final int len = value.length;
/* Now check if there are any characters that need to be changed. */
scan: {
for (firstUpper = 0 ; firstUpper < len; ) {
char c = value[firstUpper];
if ((c >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE)
&& (c <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE)) {
int supplChar = codePointAt(firstUpper);
if (supplChar != Character.toLowerCase(supplChar)) {
break scan;
}
firstUpper += Character.charCount(supplChar);
} else {
if (c != Character.toLowerCase(c)) {
break scan;
}
firstUpper++;
}
}
return this;
}
char[] result = new char[len];
int resultOffset = 0; /* result may grow, so i+resultOffset
* is the write location in result */
/* Just copy the first few lowerCase characters. */
System.arraycopy(value, 0, result, 0, firstUpper);
String lang = locale.getLanguage();
boolean localeDependent =
(lang == "tr" || lang == "az" || lang == "lt");
char[] lowerCharArray;
int lowerChar;
int srcChar;
int srcCount;
for (int i = firstUpper; i < len; i += srcCount) {
srcChar = (int)value[i];
if ((char)srcChar >= Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE
&& (char)srcChar <= Character.MAX_HIGH_SURROGATE) {
srcChar = codePointAt(i);
srcCount = Character.charCount(srcChar);
} else {
srcCount = 1;
}
if (localeDependent ||
srcChar == '\u03A3' || // GREEK CAPITAL LETTER SIGMA
srcChar == '\u0130') { // LATIN CAPITAL LETTER I WITH DOT ABOVE
lowerChar = ConditionalSpecialCasing.toLowerCaseEx(this, i, locale);
} else {
lowerChar = Character.toLowerCase(srcChar);
}
if ((lowerChar == Character.ERROR)
|| (lowerChar >= Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT)) {
if (lowerChar == Character.ERROR) {
lowerCharArray =
ConditionalSpecialCasing.toLowerCaseCharArray(this, i, locale);
} else if (srcCount == 2) {
resultOffset += Character.toChars(lowerChar, result, i + resultOffset) - srcCount;
continue;
} else {
lowerCharArray = Character.toChars(lowerChar);
}
/* Grow result if needed */
int mapLen = lowerCharArray.length;
if (mapLen > srcCount) {
char[] result2 = new char[result.length + mapLen - srcCount];
System.arraycopy(result, 0, result2, 0, i + resultOffset);
result = result2;
}
for (int x = 0; x < mapLen; ++x) {
result[i + resultOffset + x] = lowerCharArray[x];
}
resultOffset += (mapLen - srcCount);
} else {
result[i + resultOffset] = (char)lowerChar;
}
}
return new String(result, 0, len + resultOffset);
}trim()方法
trim方法是去除前或后无效空格。 通过两个循环,一个从前开始,一个从后开始来寻找空格。
public String trim() {
int len = value.length;
int st = 0;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
while ((st < len) && (val[st] <= ' ')) {
st++;
}
while ((st < len) && (val[len - 1] <= ' ')) {
len--;
}
return ((st > 0) || (len < value.length)) ? substring(st, len) : this;
}toCharArray()方法
该方法是用于将字符串复制为一个新的字符数组。
public char[] toCharArray() {
// Cannot use Arrays.copyOf because of class initialization order issues
char result[] = new char[value.length];
System.arraycopy(value, 0, result, 0, value.length);
return result;
}intern方法
native关键字是一个用于修饰原生态方法。作用是实现其他接口的语言如(c/c++)。
public native String intern();总结
相关内容
如果你觉得这篇文章对你有所帮助,欢迎赞赏~
赞赏